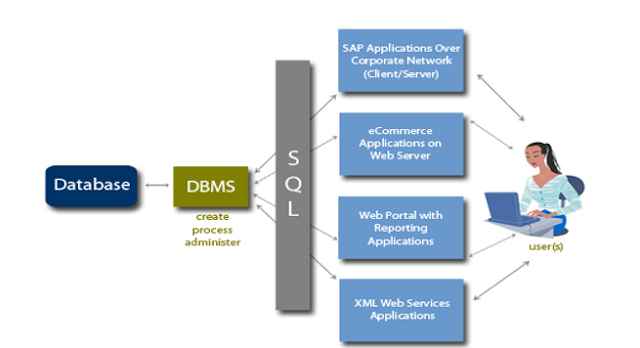
DBMS
“DATABASE MANAGEMENT SYSTEM”
“A SYSTEM WHICH MANAGES DATABASE KNOWN AS DBMS”
DBMS:
A database management system (DBMS) is a computer software application that interacts with the user, other applications, and the database itself to capture and analyze
RDBMS
A relational database management system (RDBMS) is a database management system (DBMS) that is based on the relational model. Example – Oracle
LEVELS OF DBMS
· Physical level: Physical representation of the DB on the computer.
· Logical level: the logical structure of the entire database as seen by DBA.
· View level: DB presents the data to the user. The data can be customized
according to the need.
DATA INDEPENDENCE
It refers to the immunity of user applications to changes made in the definition and organization of data.
SCHEMA
The design of a database is called the schema.
· Physical schema the design of a database at the physical level is called
physical schema, how the data stored in blocks of storage is described at this level.
· Logical schema Design of database at logical level is called logical schema,
Programmers and database administrator’s work at this level.
INSTANCE
The data stored in the database at a particular moment of time is called an instance of the database.
DATA MODELS
It defines how data is connected to each other and how they are processed and stored inside the system.
TYPES OF DATA MODELS
- Object-Oriented Model
- Hierarchical Model
- Network Model
- E R Model
- Relational Model
1. Object-Oriented Model:
o In this model, data is represented in terms of object and class.
o UML (Unified modeling language): it describes a set of diagrams and symbols that can be used to graphically model a system.
2. Hierarchical Model
o Trees of records: A hierarchical database model is a data model in which the data is organized into a tree-like structure.
It supports one-to-many relationships.
o Limitation this model does not support many to many relationships.
3. Network Model
o Similar to the hierarchical database with the implementation of many-to-many relationships
4. E-R MODEL (ENTITY RELATIONSHIP MODEL)
o It is a way of graphically representing the logical relationships of entities (or objects) in order to create a database.
o Entities: it can be any real world thing like Object, Concept or event (subject) (Example customer, student, car etc.)
o Entity set: it is a set of entities that share same properties.
o Weak entity set: entity set that does not have the primary key is referred as weak entity set.
5. Relationships :
o One to One
o One to Many
o Many to One
o Many to Many
QUESTIONS
Q.1. Full form of RDBMS?
a) Rare database management system
b) Relational database management system
c) Real DBMS
d) None of these
Ans.(B)
Q.2. What Is SCHEMA?
A) Levels in database
B) Content of database
C) Logical structure of database
D) None of these
Ans.(C)
Q.3. HOW MANY VIEWS AVAILABLE IN DATABASE?
A) 1 B) 2 C) 3 D) 4
Ans.(C)
Q.4. Which of the following items is not a DBMS:
A) Access B) Acrobat Reader C) Oracle D) SQL Server
Ans.(B)
Q.5. The database design that uses a hierarchical data structure, but incorporates multiple data entry points is called a:
A) Hierarchical database
B) Network database
C) Object oriented database
D) Relational database
Ans.(B)
Q.6. Which of the following is an extension of the Relational Database model?
A) Hierarchical database
B) Multidimensional database
C) Network database
D) Object oriented database
Ans.(D)
Q.7. What is the main strength of Relational Databases?
A) Ability to handle any type of data
B) Defining objects provides for reuse of data definitions
C) Ease of use
D) Flexibility and efficiency in accessing data
Ans.(D)
Q.8. Which component of the database management system (DBMS) most affects the performance (speed)?
A) Data Storage Subsystem
B) Database Engine
C) Query Processor
D) Security Subsystem
Ans.(B)
Q.9. Data integrity can be improved by which of the following means ______.
A) Adding indexes
B) Entering appropriate terms into the data dictionary
C) Incorporating business rules when defining the data
D) Using inheritance
Ans.(C)
Q.10. The role of the query system is to:
A) Present the data in a user-friendly format
B) Provide data security
C) Retrieve and manipulate data
D) Support data integrity
Ans.(C)